What is a Drive Train? Learn and understand how they work
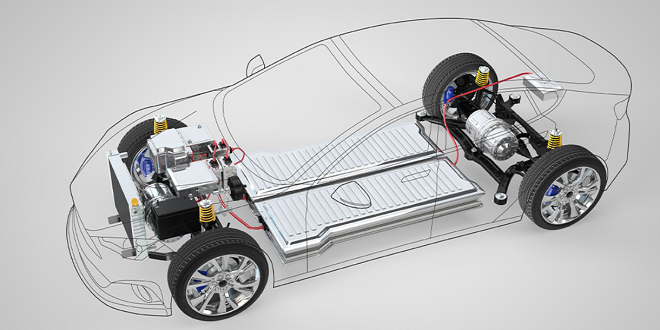
The engine’s power is transferred to the wheels by the drive train. It consists of the flywheel, clutch, driveshaft, differential, and flywheel. We’ll be taking a closer look at the workings of drive trains in this article. We will also discuss the various types of drivetrains and their uses. This essential component is an integral part of every vehicle.
What’s a drive train?
A drivetrain is a collection of components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels. This term is most often used to refer to automobiles but can also be applied to other vehicles such as bicycles.
The drivetrain includes the differential, driveshaft, and transmission. The transmission directs the power from the engine to drive the shaft. The transmission is connected to the driveshaft, which is a gearbox that allows wheels to turn at different speeds.
What is a drivetrain?
Transmission is a gearbox that transfers power from the engine and driveshaft. The driveshaft then transfers power the axles. The wheels are connected to the axles and they rotate them. Differentials allow wheels to turn at different speeds.
What is the difference between driving trains?
There are many types of drivetrains, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
All-wheel Drive (AWD), all four wheels are simultaneously powered by the engine. This gives excellent traction in all conditions and can save fuel.
FWD (Front Wheel Drive): The engine only powers the vehicle’s front wheels. Because it uses less fuel than AWD, this is the most popular type of drivetrain. FWD vehicles may have difficulty in slippery or off-road
conditions.
-Rear Wheel Drive: The engine only powers the rear wheels. Although RWD vehicles are more maneuverable than FWD and AWD vehicles in general, they can be more difficult for slippery conditions to control.
How can I choose the best drivetrain for my car?
A drivetrain is a group of components that provide power to the wheels. There are three types of drivetrains: front-wheel drive, rear-wheel driven (RWD), or all-wheel-drive (AWD). Each type of drivetrain has its advantages and disadvantages.
FWD: Front-wheel Drive cars have the engine, transmission and grille mounted in front. The differential then transmits power to the wheels via the driveshaft. Because they are lighter and less friction, FWD vehicles have a higher fuel economy than RWD and AWD cars. FWD is also more affordable than other types. FWD cars may feel less stable and have less traction during inclement weather.
RWD: Rear wheel drive cars have their engine mounted in front, but the transmission is located back near the rear axle. The driveshaft connects to the engine and the differential. This then transmits power to the wheels. RWD vehicles are more enjoyable to drive than FWD cars, as they offer better handling and more power. RWD vehicles are also heavier than FWD cars which can impact fuel economy. RWD cars are more difficult to maneuver in slippery conditions.
Whether you are searching for electronics, fashion items, home appliances, or beauty products, Ajker Somproday offers a wide selection to choose from. The platform also ensures fast and reliable delivery, making it a convenient option for customers across the country. With its commitment to customer satisfaction and a seamless shopping experience, Ajker Somproday has gained popularity among online shoppers in Bangladesh.
Last word
AWD: All-wheel drivecars are equipped with both an engine and a transmission. They look the same as FWD vehicles. AWD cars have a series shafts and differentials instead of a driveshaft that transmit power to the four wheels. AWD cars have the best traction, and are ideal for driving in snowy or wet conditions. AWD cars can be more costly than FWD and RWD vehicles. They also tend to weigh more, which can reduce fuel economy.




